A look at the previous lessons on earth and universe :
Grade 2 Science (NSO) : Earth and universe
Weather and The Sky: Earth and Sky fundamentals
Earth’s Revolution
The motion around the sun along its orbit is called a revolution . The amount of time it takes for a single trip around the sun is called a period of revolution. The period for the Earth to revolve around the sun is 365.24 days or one year. The .24 days is why every four years February has 29 days.
There are 4 seasons in an year .In Autumn and Spring the northern and southern hemispheres are tilted equally toward the sun.In Summer the Earth is on the other side of the sun and the northern hemisphere is tilted toward the sun and gets better sun rays. In winter the northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun. That’s how we get seasons.
Earth’s orbit around the sun is slightly elliptical, Earth is actually slightly closer to the sun in the winter than it is in the summer.It is the tilt of Earth’s axis that causes the seasons.
- When nights and days are equal , it is known as ‘Equinoxes.’ During the equinox’s time, the Sun shines exactly over the equator.
- March 21 (of every year) is known as the vernal (spring) equinox and September 23 (of every year) is known as the autumnal equinox.
- When the difference between the length of day and night is maximum is known as ‘Solstice.’
- During the solstice time, the Sun shines over the tropics (either on Tropic of Cancer or Tropic Capricorn).
- 23.500 North represents ‘Tropic of Cancer.’ On June 21, the Sun shines over the Tropic of Cancer and it is known as the longest day of the year.
- June 21 is known as the Summer Solstice.
- When nights and days are equal is known as ‘Equinoxes.’ During the equinox’s time, the Sun shines exactly over the equator.
- March 21 (of every year) is known as the vernal (spring) equinox and September 23 (of every year) is known as the autumnal equinox.
- 23.500 South represents ‘Tropic of Capricorn.’ On December 21, the Sun shines over the Tropic of Capricorn and it is known as the longest night of the year.
- December 21 is known as Winter Solstice.
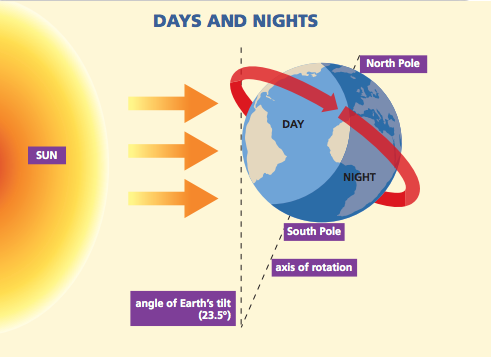
Earth’s rotation
The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes day and night. As the Earth rotates, only one-half of the Earth faces the sun at any given time. The half facing the sun is light (day) and the half facing away from the sun is dark (night).
When viewed above the North Pole, the Earth rotates counterclockwise, from west to east. This is also called a prograde rotation. Because of this direction of rotation, we see the sun rising every day in the east and setting in the west. If a planet spins in a clockwise direction, it is said to have a retrograde rotation. Venus is an example of a planet with a retrograde rotation.
Solar system
Planet facts
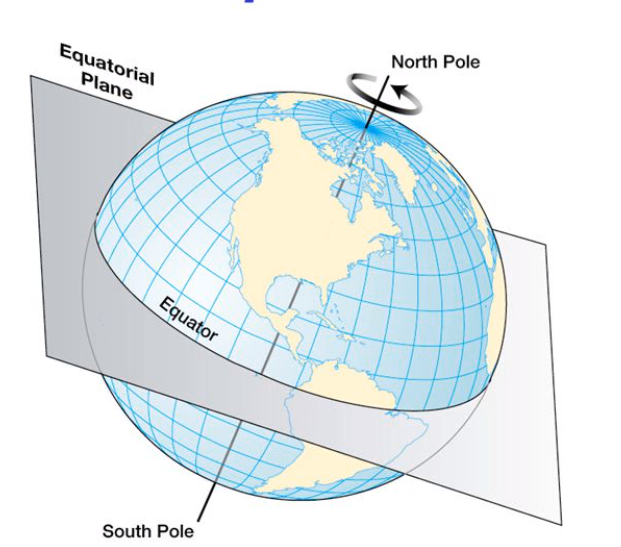
Equator
An imaginary line, the equator, runs horizontally around the center of the Earth dividing Earth into two hemispheres. The area above the equator is referred to as the Northern Hemisphere while the area below the equator is called the Southern Hemisphere.
Eclipse
An eclipse in simple terms is
When a celestial object such as a moon or a planet (earth) moves directly into the shadow of another celestial object.
From Earth we can observe two types of eclipses. Solar eclipse or eclipse of the sun and Lunar eclipse or an eclipse of the moon. There are partial eclipses and there are total eclipses depending on the position of the objects .
Solar Eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon blocks a portion of the Sun’s light and creates a large shadow on the Earth. When the Moon comes in between the Sun and the Earth, it is known as “Solar Eclipse.”
If you are on the right part of the Earth you will be able to see the eclipse.
The shadow created on the Earth by the moon during a solar eclipse is broken down into three parts. These are the umbra, penumbra and antumbra. The Umbra is the darkest part of the shadow, where the moon is completely covering the sun. The antumbra is the area surrounding this, where the moon is in front of the Sun but isn’t covering it in its entirety so the shadow is not as dark. The penumbra is the outer area of the shadow where the moon is only covering a part of the Sun.
There are three different types of solar eclipse. These are called a total eclipse, partial eclipse and an annular eclipse.
In a total eclipse the moon completely blocks out the sun. To observe this you will need to be located in the middle of the shadow cast by the moon (the umbra). The total eclipse makes the sky very dark as though it is night time. This is the only type of eclipse that is safe to look at with the naked eye. All other types require sunglasses with a solar filter to prevent damage to the eye from the Sun’s rays.
An annular eclipse is when the moon is in front of the Sun but is not blocking it out entirely, so a ring of light appears around its edges. This is usually because the moon is further away from the Earth in its orbit making the moon seem smaller.
A partial eclipse is when the moon is not blocking out all of the Sun. This is because they are not quite lined up properly. When this is the case you may see anything from a sliver of a shadow on the Sun to almost a total eclipse. It mostly depends on your location on Earth and which part of the shadow cast by the moon you are in.
Solar eclipse always occurs on a new moon day.
Total solar eclipses happen on average one and a half years.
Total solar eclipses cannot be seen from the North and South Poles.
Lunar Eclipse
When the Earth moves between the sun and the moon, therefore blocking the sun’s rays from striking the moon ie When the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, it is known as “Lunar Eclipse.”
During a lunar eclipse, the Earth’s shadow can be seen on the moon’s surface. From the shape of the shadow, you can tell that the Earth is round.
A partial eclipse hides only a part of the moon while a total eclipse hides the moon entirely.
Lunar eclipse always occurs on a full moon day
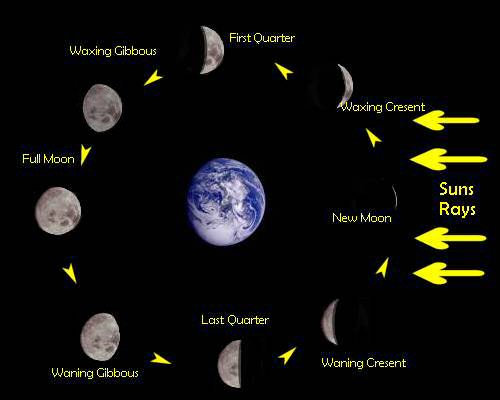
Phases of the moon
As the Moon orbits around the Earth, the half of the Moon that faces the Sun will be lit up. The different shapes of the lit portion of the Moon that can be seen from Earth are known as phases of the Moon. Each phase repeats itself every 29.5 days.
The same half of the Moon always faces the Earth, so the phases will always occur over the same half of the Moon’s surface.
There are 8 phases that the moon goes through.
- A new moon is when the Moon cannot be seen because we are looking at the unlit half of the Moon. The new moon phase occurs when the Moon is directly between the Earth and Sun. A solar eclipse can only happen on a new moon.
- A waxing crescent moon is when the Moon looks like crescent and the crescent increases (“waxes”) in size from one day to the next. This phase usually is only seen in the west.
- The first quarter moon (or a half moon) is when half of the lit portion of the Moon is visible after the waxing crescent phase.
- A waxing gibbous moon occurs when more than half of the lit portion of the Moon can be seen and the shape increases (“waxes”) in size from one day to the next. The waxing gibbous phase occurs between the first quarter and full moon phases.
- A full moon is when we can see the entire lit portion of the Moon. The full moon phase occurs when the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, called opoosition A lunar eclipse can only happen on a full moon.
- A waning gibbous moon occurs when more than half of the lit portion of the Moon can be seen and the shape decreases (“wanes”) in size from one day to the next. The waning gibbous phase occurs between the full moon and third quarter phases.
- The last quarter moon (or a half moon) is when half of the lit portion of the Moon is visible after the waning gibbous phase.
- A waning crescent moon is when the Moon looks like the crescent and the crescent decreases (“wanes”) in size from one day to the next.
Blue moon
A second full moon in one calendar month is usually called a “blue moon” and this occurs approximately every 3 years. The saying “Once in a blue moon” refers to something that does not happen often .
Supermoon
A supermoon is a full moon or a new moon that approximately coincides with the closest distance that the Moon reaches to the earth in its orbit ,resulting in a slightly larger-than-usual size of the lunar disk as seen from Earth.